Không có sản phẩm trong giỏ hàng!
What are Shells in 3D Printing?
- Abdulrahman Alhamed
- 18 Jun 2023
- Tutorial
- Beginner
- 1300
One crucial aspect of 3D printing that significantly influences the quality and functionality of printed objects is the concept of shells. Shells, also known as outer perimeters or contours, refer to the outermost layers of a 3D-printed object. Understanding the role of shells is vital for achieving optimal print results and ensuring the desired characteristics of the final product. The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of shells in 3D printing. We will explore the definition, importance, and various considerations associated with shell design.
What Are Shells?
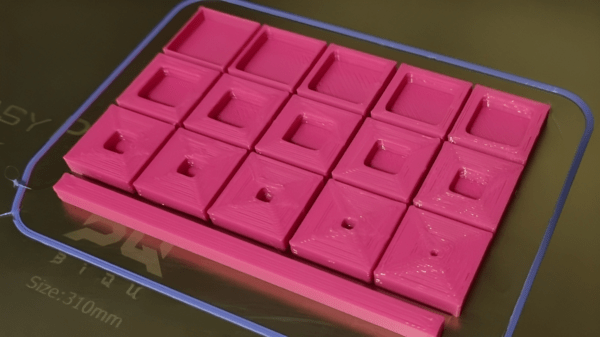
Source: Che Simons via All3DP
In the context of 3D printing, shells refer to the outermost layers or contours of a printed object. They define the external shape and surface of the object, providing its visual appearance and contributing to its structural integrity.
Relationship Between Shells and Infill
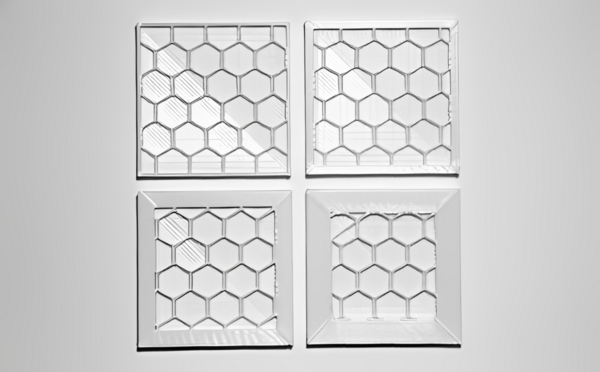
Source: microfabricator
Infill plays a crucial role in 3D printing, as it fills the space between the inner and outer shells, providing internal support and strength to the printed object. The infill consists of a pattern of interconnected lines, grids, or solid structures that add structural integrity and prevent the object from being hollow or fragile.
The relationship between shells and infill is interconnected. While shells determine the outer appearance and define the overall shape, the infill provides internal support and affects the structural integrity of the object. Finding the right balance between shell thickness and infill density is essential for achieving the desired strength, weight, and print time for a given object.
Impact of Shell Thickness
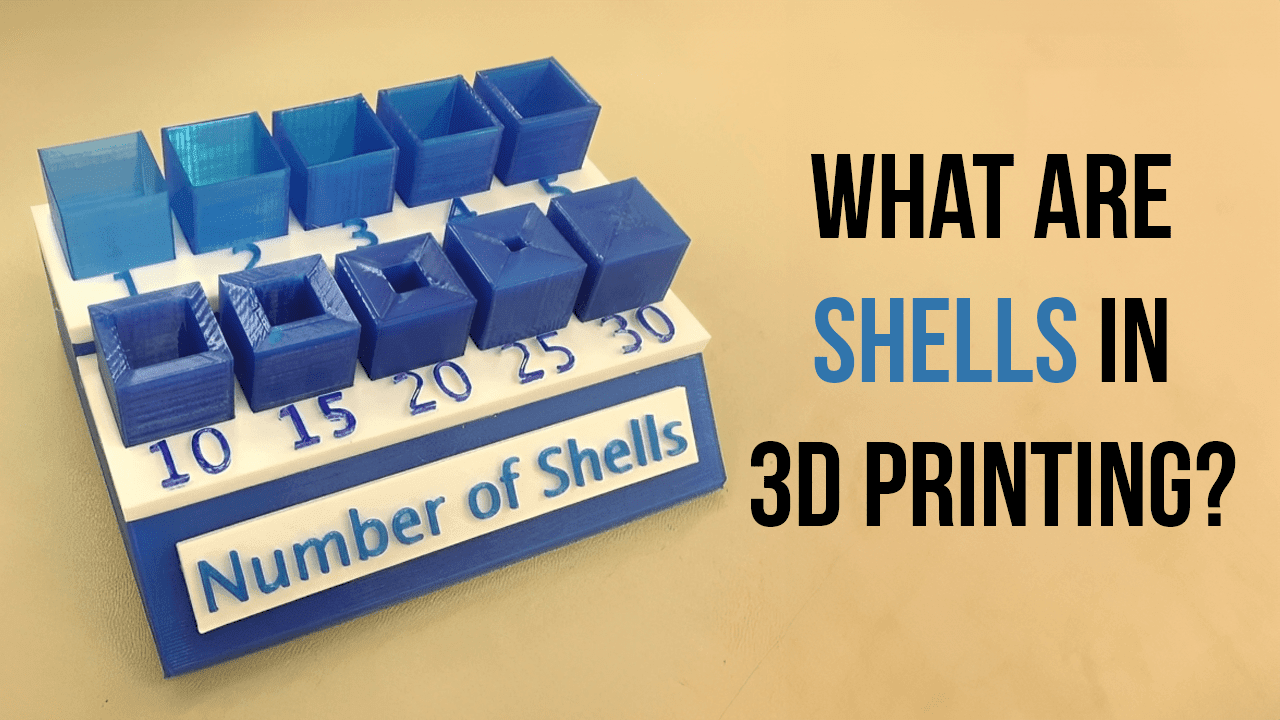
Source: learn.thestempedia
Strength and Durability: Thicker shells generally result in stronger and more robust objects. A thicker outer shell provides increased structural integrity, making the object less prone to deformation or breakage. This is particularly important for functional parts or objects that need to withstand mechanical stress or external forces.
Print Detail: On the other hand, thinner shells allow for finer print detail and intricate features. With thinner shells, the layer lines and transitions between layers become less noticeable, resulting in smoother surfaces and better visual appeal. Thinner shells are often favored for aesthetic or decorative objects where intricate designs or surface finishes are paramount.
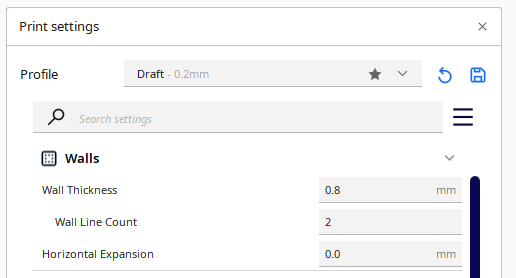
Adjusting Shell Thickness in Cura
- Locate the Shell settings in Cura. This can typically be found in the sidebar.
- Adjust the "Wall Line Count" or "Wall Thickness" parameter to control the number of outer shell lines or the overall thickness of the outer shell. Increasing the value will result in thicker shells, while decreasing it will create thinner shells.
- Fine-tune the shell settings to achieve the desired balance between strength, print detail, and print time. Experiment with different values to find the optimal setting for your specific project.
Conclusion
Shells in 3D printing play a crucial role in defining the outer layers of printed objects, influencing their strength, durability, and visual quality. By adjusting the shell thickness, users can customize the balance between strength and detail, with thicker shells offering enhanced robustness and thinner shells allowing for finer print resolution. Utilizing slicing software like Cura provides further control over shell settings, enabling users to optimize their 3D prints for specific requirements.
 International
International Singapore
Singapore Malaysia
Malaysia Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam